The only tool that validates your ELISA kit
through scientific literature, based on comparable experiments.
Eliminate hours of manual literature review, and validate your material and its variables in minutes!

How it works
When buying a lab product or setting up its associated variables, our AI-driven agent helps you validate your choice by analyzing published research with an unbiased methodology.
Using AI-powered similarity search, it examines comparable experiments to yours, checking the usage of your selected product—or alternative options—along with their frequency and associated variables.
Why it works
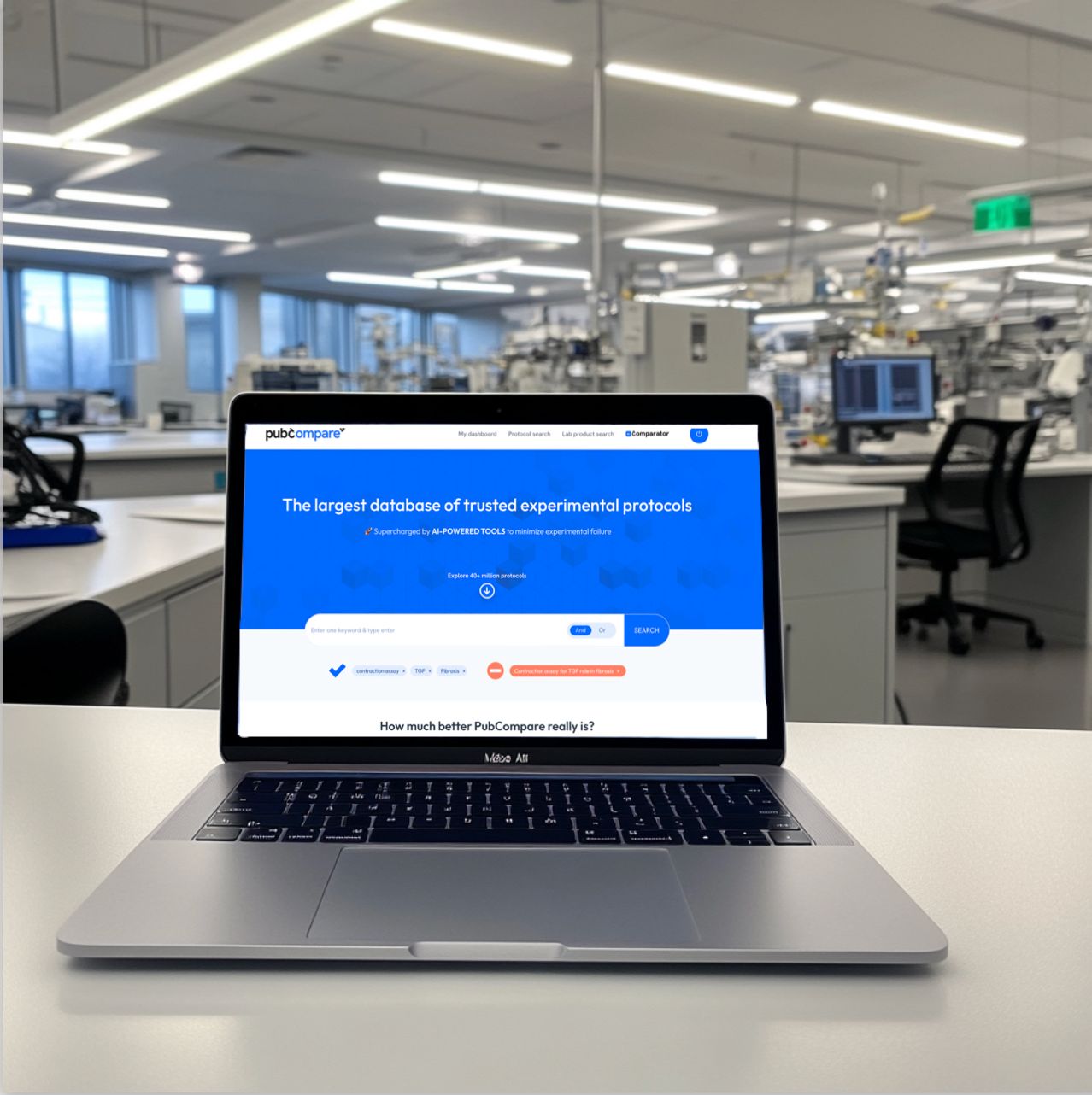
- Powered by the largest database of experimental protocols, with 40 million methods sourced from publications, preprints, patents, and the websites of major lab equipment providers.
- Keywords and traditional filters aren’t enough. A chat agent combined with AI similarity search ensures you get the most relevant results—quickly and accurately—so you never miss valuable details.
Lab product search by name
This version features over 1,000,000 products from 2,000 Product Manufacturers
We found 0 results to your query
Try another search with keywords variations such as synonyms, singular, plural, etc.